Rechargeable batteries have become an integral part of our modern lives. From powering our smartphones and laptops to running electric vehicles, these portable energy sources have revolutionized the way we live and work. But have you ever wondered how they actually work? In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of rechargeable batteries and uncover the science behind their operation.
First, let’s understand the basics. Rechargeable batteries, also known as secondary batteries, are designed to be reused multiple times. Unlike disposable batteries, which are single-use and must be discarded after depletion, rechargeable batteries can be recharged by applying an electric current to them. This ability to recharge sets them apart and makes them a more sustainable and cost-effective option in the long run.
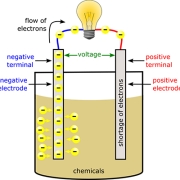
To grasp the inner workings of rechargeable batteries, we need to explore their key components. At the heart of these powerhouses are electrochemical cells. These cells consist of two electrodes, an anode (negative electrode) and a cathode (positive electrode), separated by an electrolyte. When the battery is being used, a chemical reaction occurs within these cells, allowing the flow of electrons from the anode to the cathode, generating an electric current.
The magic lies in the reversible nature of this chemical reaction. When the battery is connected to a power source, such as a charger, the flow of electrons is reversed. This process, known as recharging, restores the chemical composition of the electrodes, allowing the battery to store energy once again.
Rechargeable batteries come in various chemistries, each with its own advantages and limitations. From lithium-ion to nickel-metal hydride, these chemistries determine factors such as energy density, voltage, and cycle life. Understanding these differences can help us choose the right rechargeable battery for our specific needs.
Now that we have scratched the surface of how rechargeable batteries work, let’s dive deeper into the intricacies of their operation. In subsequent articles, we will explore the different types of rechargeable batteries, their applications, and the environmental impact of their usage. So, stay tuned for an enlightening journey into the world of rechargeable batteries and discover the power within these remarkable energy sources.
How Do Rechargeable Batteries Work?
Rechargeable batteries have become an essential part of our daily lives, powering everything from our smartphones to electric vehicles. But have you ever wondered how these batteries actually work? In this article, we will delve into the inner workings of rechargeable batteries and explore the science behind their ability to store and release energy.
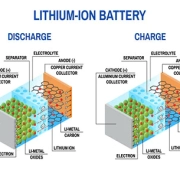
At the heart of a rechargeable battery are two key components: the cathode and the anode. These electrodes are separated by an electrolyte, which allows ions to flow between them. When the battery is being charged, an electric current is applied to the battery, causing the ions to move from the cathode to the anode. This process is known as oxidation. During this phase, the battery stores energy.
When it comes time to use the battery, the process is reversed. The stored energy is released as the ions move from the anode back to the cathode. This process is known as reduction. The movement of ions creates an electric current that can power a device or vehicle.
One of the key advantages of rechargeable batteries is that they can be recharged multiple times. This is made possible by the use of reversible reactions at the electrodes. During charging, the reactions are driven in one direction, while during discharging, they are driven in the opposite direction. This allows the battery to be charged and discharged repeatedly without significant degradation in performance.
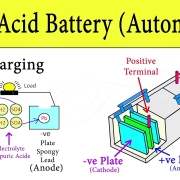
Rechargeable batteries come in various chemistries, including lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, and lead-acid. Each chemistry has its own unique properties and characteristics, making them suitable for different applications.
In conclusion, rechargeable batteries work by utilizing reversible reactions between the cathode and anode, allowing them to store and release energy multiple times. Understanding the inner workings of these batteries is crucial as they continue to power our modern world.
What Are the Different Types of Rechargeable Batteries?
Rechargeable batteries have become an essential part of our daily lives, powering everything from our smartphones to electric vehicles. But have you ever wondered about the different types of rechargeable batteries available in the market? In this article, we will explore the various types of rechargeable batteries and how they work.
1. Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries:
NiCd batteries have been around for decades and are known for their high energy density. They are commonly used in portable electronics, power tools, and medical devices. However, they suffer from the “memory effect” and contain toxic cadmium, making them less environmentally friendly.
2. Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries:
NiMH batteries are an improvement over NiCd batteries as they offer higher energy density and do not suffer from the memory effect. They are commonly used in digital cameras, cordless phones, and hybrid cars. NiMH batteries are also more environmentally friendly as they do not contain toxic metals.
3. Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries:
Li-ion batteries are widely used in smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles due to their high energy density and long cycle life. They offer a lightweight and compact design, making them ideal for portable devices. Li-ion batteries do not suffer from the memory effect and have a low self-discharge rate.
4. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) Batteries:
LiPo batteries are a variation of Li-ion batteries that use a polymer electrolyte instead of a liquid electrolyte. They are commonly used in drones, wearable devices, and remote-controlled vehicles. LiPo batteries offer high energy density, lightweight design, and flexibility in shape.
In conclusion, rechargeable batteries come in various types, each with its own advantages and applications. Whether it’s the high energy density of NiCd batteries, the eco-friendliness of NiMH batteries, or the versatility of Li-ion and LiPo batteries, there is a rechargeable battery for every need. Understanding the different types of rechargeable batteries can help you make informed choices when it comes to powering your devices efficiently and sustainably.
How Long Do Rechargeable Batteries Last?
Rechargeable batteries have become an essential part of our daily lives, powering everything from our smartphones to electric vehicles. As we rely more on these batteries, it’s natural to wonder how long they will last before needing to be replaced.
The lifespan of a rechargeable battery depends on several factors, including its chemistry, usage patterns, and maintenance. The most common types of rechargeable batteries are nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd), nickel-metal hydride (Ni-MH), and lithium-ion (Li-ion).
Ni-Cd batteries, although less common nowadays due to environmental concerns, can last for approximately 500-1000 charge cycles. A charge cycle refers to the process of fully discharging and then recharging the battery. On the other hand, Ni-MH batteries can typically handle around 500-1000 charge cycles as well.
Lithium-ion batteries, which are widely used in smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles, offer a longer lifespan compared to Ni-Cd and Ni-MH batteries. They can last for approximately 300-500 charge cycles. However, it’s important to note that the actual lifespan of a lithium-ion battery can vary based on usage and charging habits.
To maximize the lifespan of rechargeable batteries, it’s recommended to avoid deep discharges and overcharging. Deep discharges, where the battery is completely drained, can lead to irreversible damage. Overcharging, on the other hand, can cause excessive heat and shorten the battery’s lifespan.
Proper storage is also crucial for extending the life of rechargeable batteries. If you’re not using a device for an extended period, it’s best to store the battery at around 40% charge in a cool and dry place.
In conclusion, the lifespan of rechargeable batteries varies depending on their chemistry and usage. While Ni-Cd and Ni-MH batteries can last for approximately 500-1000 charge cycles, lithium-ion batteries offer a longer lifespan of around 300-500 charge cycles. By following proper charging and storage practices, you can maximize the lifespan of your rechargeable batteries and get the most out of them.
What Are the Advantages of Rechargeable Batteries?
Rechargeable batteries have become increasingly popular in recent years, and for good reason. They offer numerous advantages over disposable batteries that make them a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly choice. In this article, we will explore the benefits of rechargeable batteries and why they are a smart choice for powering your devices.
One of the key advantages of rechargeable batteries is their long-term cost savings. While they may have a higher upfront cost compared to disposable batteries, rechargeable batteries can be reused hundreds, if not thousands, of times. This means that over time, they can save you a significant amount of money. Additionally, rechargeable batteries tend to have a higher energy capacity than disposable batteries, allowing them to power devices for longer periods before needing to be recharged.
Another advantage of rechargeable batteries is their positive impact on the environment. Disposable batteries contribute to pollution and waste as they are thrown away after a single use. In contrast, rechargeable batteries can be recharged and reused multiple times, reducing the amount of battery waste that ends up in landfills. By choosing rechargeable batteries, you are actively reducing your carbon footprint and helping to preserve the environment for future generations.
Furthermore, rechargeable batteries are more convenient and reliable. With disposable batteries, there is always the risk of running out of power at an inconvenient time and needing to find replacements. Rechargeable batteries can be easily recharged using a charger, ensuring that you always have a power source available when you need it. This makes them particularly useful for high-drain devices such as cameras, smartphones, and remote controls.
In conclusion, rechargeable batteries offer several advantages over disposable batteries. They are cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and convenient to use. By making the switch to rechargeable batteries, you can save money, reduce waste, and have a reliable power source for your devices. So why not make the smart choice and start using rechargeable batteries today?
How Do Rechargeable Batteries Store and Release Energy?
Rechargeable batteries have become an essential part of our lives, powering a wide range of devices from smartphones to electric vehicles. But have you ever wondered how these batteries store and release energy? In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of rechargeable batteries and explore the science behind their operation.
At the heart of a rechargeable battery is a chemical reaction that allows the storage and release of electrical energy. Unlike disposable batteries, which are designed for single-use, rechargeable batteries can be recharged multiple times, making them more cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
The key component of a rechargeable battery is the electrochemical cell. This cell consists of two electrodes – a positive electrode called the cathode and a negative electrode called the anode. These electrodes are immersed in an electrolyte solution, which allows the flow of ions between them.
During the charging process, electrical energy is supplied to the battery, causing a chemical reaction to occur. This reaction converts the chemical energy into electrical energy, which is stored in the battery. The positive electrode, or cathode, undergoes a reduction reaction, while the negative electrode, or anode, undergoes an oxidation reaction.
When the battery is discharged, the stored electrical energy is released. The chemical reactions are reversed, with the cathode releasing electrons and the anode accepting them. This flow of electrons creates an electric current that can power various devices.
One of the most common types of rechargeable batteries is the lithium-ion battery. These batteries use lithium ions to transport charge between the electrodes. They are lightweight, have a high energy density, and can be recharged numerous times without significant loss of capacity.
In conclusion, rechargeable batteries store and release energy through chemical reactions that occur within the electrochemical cell. Understanding the inner workings of these batteries helps us appreciate their importance in our modern lives and encourages us to use them responsibly to minimize environmental impact.
Can Rechargeable Batteries Be Overcharged?
Rechargeable batteries are a convenient and cost-effective solution for powering our devices. Whether it’s our smartphones, laptops, or electric vehicles, these batteries play a crucial role in our daily lives. But can they be overcharged? Let’s delve into the working of rechargeable batteries to find out.
Rechargeable batteries, also known as secondary batteries, work on the principle of reversible chemical reactions. They consist of two electrodes, an anode, and a cathode, separated by an electrolyte. When the battery is charged, the chemical reactions occur in reverse, allowing the battery to store energy.
One common type of rechargeable battery is the lithium-ion battery. It is widely used due to its high energy density and long lifespan. However, overcharging a lithium-ion battery can lead to detrimental effects. The excess charging causes the lithium ions to move rapidly between the electrodes, leading to the formation of metallic lithium. This can cause the battery to overheat, leading to reduced performance, shortened lifespan, and in extreme cases, even explosions.
To prevent overcharging, most rechargeable batteries are equipped with a protection circuit. This circuit monitors the battery’s voltage and temperature, cutting off the charging process when the battery reaches its maximum capacity. This helps to prevent overcharging and ensures the longevity of the battery.
It is important to note that not all rechargeable batteries are created equal. Different types of batteries have different charging characteristics and require specific charging methods. It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and use the recommended charger to avoid overcharging.
In conclusion, rechargeable batteries can be overcharged, especially lithium-ion batteries. To ensure the optimal performance and safety of your rechargeable batteries, it is essential to follow the recommended charging guidelines and use the appropriate charger. By doing so, you can enjoy the convenience and longevity that rechargeable batteries offer.
What Is the Best Way to Dispose of Rechargeable Batteries?
Rechargeable batteries have become an essential part of our lives, powering everything from our smartphones to electric vehicles. But what happens when these batteries reach the end of their life cycle? How should we dispose of them properly? Let’s explore the best way to handle the disposal of rechargeable batteries.
Firstly, it’s important to note that rechargeable batteries contain harmful chemicals such as lead, cadmium, and mercury. These substances can pose a significant risk to the environment and human health if not handled correctly. Therefore, it is crucial to dispose of them responsibly.
One option for disposing of rechargeable batteries is to recycle them. Many electronic stores and recycling centers offer drop-off points specifically for batteries. Recycling not only helps prevent hazardous materials from ending up in landfills but also allows valuable metals like lithium and cobalt to be recovered and reused in the production of new batteries.
Another option is to participate in a take-back program. Some battery manufacturers have established programs that allow consumers to return their used batteries for proper disposal. These programs ensure that the batteries are handled in an environmentally friendly manner.
When it comes to rechargeable batteries, it’s important to avoid throwing them in the regular trash. This can lead to the batteries ending up in landfills, where they can leak harmful chemicals into the soil and water. Instead, make use of the available recycling options or take-back programs.
In conclusion, the best way to dispose of rechargeable batteries is through recycling or participating in a take-back program. By doing so, we can protect the environment, prevent the release of hazardous materials, and promote the reuse of valuable resources. Let’s all do our part in ensuring the proper disposal of rechargeable batteries.
Are Rechargeable Batteries Environmentally Friendly?
Rechargeable batteries have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their ability to be reused multiple times, reducing the need for single-use disposable batteries. But are rechargeable batteries really environmentally friendly? Let’s explore how these batteries work and their impact on the environment.
Rechargeable batteries, also known as secondary batteries, work by converting chemical energy into electrical energy. They are made up of one or more electrochemical cells, which consist of positive and negative electrodes immersed in an electrolyte solution. During the charging process, the chemical reactions within the battery reverse, allowing it to store electrical energy. When the battery is discharged, the reactions occur in the opposite direction, releasing the stored energy.
One of the main advantages of rechargeable batteries is that they can be used multiple times, reducing the number of batteries that end up in landfills. This helps to minimize the environmental impact associated with the disposal of single-use batteries, which often contain toxic chemicals such as mercury, cadmium, and lead.
However, rechargeable batteries are not without their environmental drawbacks. The production and disposal of rechargeable batteries can still have a significant impact on the environment. The manufacturing process requires the extraction of raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can have environmental and social consequences. Additionally, the recycling of rechargeable batteries can be complex and expensive.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, it is crucial to properly dispose of rechargeable batteries at designated recycling centers. This ensures that valuable materials can be recovered and reused, minimizing the need for new resource extraction.
In conclusion, while rechargeable batteries offer a more sustainable alternative to single-use batteries, they are not entirely environmentally friendly. Proper disposal and recycling practices are essential to reduce their impact on the environment. By using rechargeable batteries responsibly, we can contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how rechargeable batteries work is essential for maximizing their lifespan and making environmentally conscious choices. Throughout this post, we have explored various aspects of rechargeable batteries, including their types, lifespan, advantages, energy storage and release, overcharging concerns, disposal methods, and environmental impact.
By delving into the working mechanism of rechargeable batteries, we have learned that they rely on reversible chemical reactions to store and release energy. This allows them to be recharged multiple times, making them a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to disposable batteries.
We have also discussed the different types of rechargeable batteries, such as nickel-cadmium, nickel-metal hydride, and lithium-ion batteries. Each type has its own characteristics and applications, and understanding these differences can help us choose the right battery for our devices.
Furthermore, we have explored the lifespan of rechargeable batteries, which can vary depending on usage and maintenance. By following proper charging and storage practices, we can extend the lifespan of our batteries and reduce waste.
The advantages of rechargeable batteries, such as cost savings, convenience, and reduced environmental impact, have been highlighted. Rechargeable batteries not only save money in the long run but also contribute to a greener future by reducing the number of disposable batteries that end up in landfills.
Looking ahead, it is crucial to stay informed about future developments and trends in rechargeable battery technology. Advancements in battery capacity, charging speed, and energy efficiency are expected to shape the market in the coming years.
In conclusion, we hope this post has provided you with valuable insights into how rechargeable batteries work and the importance of making informed choices. Remember to dispose of your batteries responsibly and consider recycling programs in your area. Thank you for reading, and we encourage you to leave any comments or feedback. Together, we can make a positive impact on the environment and embrace the benefits of rechargeable batteries.